If you’ve ever lost power in your home, then you know how troublesome it can be. Whether it’s due to a major storm or a downed power line in your area, you never know if the power will be down for minutes, hours or days.
And not only that can be harmful, but it can also be dangerous. That’s where the generator (or battery backup) comes in.
Having a generator handy to energy your house (or something else) can be a game changer. But the first step is to pick out the proper generator for you. It’s miles critical to do your studies and apprehend precisely what you need.
It’s also vital to understand a number of the protection worries that include generators, inclusive of the opportunity of carbon monoxide poisoning.
In this guide, we’re diving into how generators work, the different types of generators, how to maintain your generator and more considerations to help you choose the right generator for your home.
What is a home generator?
A generator is a device that can provide you with electricity for your home, business or when you are travelling. Despite what the name implies, generators do not produce electricity. Instead, they take some form of energy and convert it into electricity.
Generators can be used to provide backup power for your home or business in the event of an outage due to inclement weather, downed power lines or any other disaster. They can also be used to provide power on the go, such as when camping or traveling in an rv.
Types of generators
When it comes to choosing a generator, you need to first narrow down the type of generator you want. The first types are portable generators, inverter generators and stationary generators.
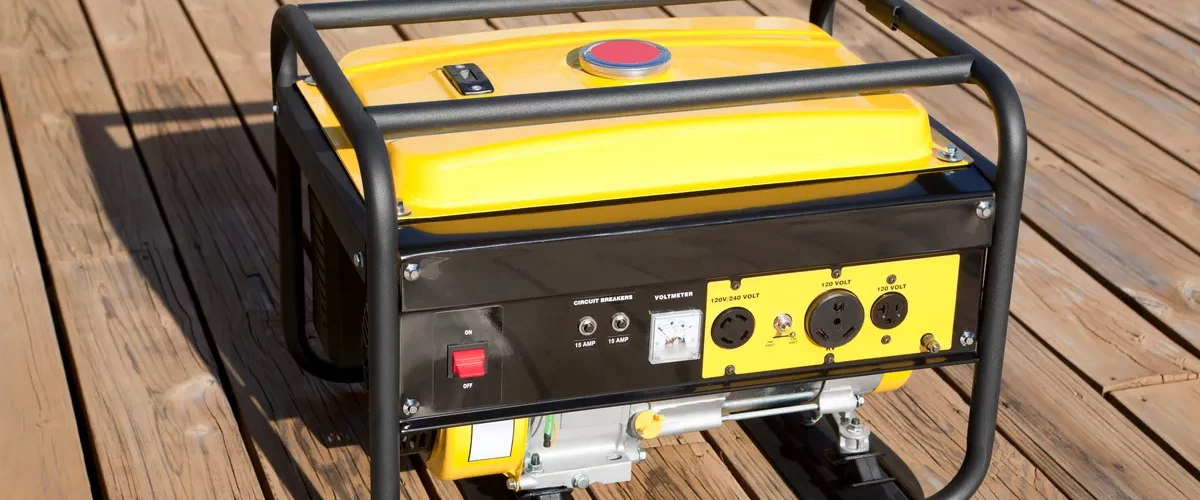
Portable generator
A transportable generator, as the call suggests, is the maximum effortlessly transportable. These turbines frequently have wheels, making them easy to transport around to deliver electricity everywhere.
Even the smallest fashions may be hand-held in preference to on wheels, making them even greater cell. Transportable mills commonly run on fuel and are generally inexpensive than stationary turbines.
Inverter generator
An inverter generator is similar to a portable generator in that it is small and easy to carry. They are also quiet, which can make them suitable for a wide range of activities, including camping and other activities.
Inverter generators and standard portable generators differ in the type of electricity they produce, the amount of power they can produce, their portability, their noise and their cost. Electric generators are usually more expensive and produce less energy, but they are portable, quieter and produce fewer emissions.
Standby generator
A standby generator is the permanent solution to a portable generator. It is big and very expensive. Rather than being easily transported, it is permanently installed in your home or business. When your power runs out, the standby generator is turned on to continue providing power.
Instead of gasoline, stationary generators are usually powered by propane, and they can also be powered by natural gas.
According to expert, a licensed electrician we spoke with, stationary generators eliminate many of the safety concerns associated with portable generators. And although it is more expensive, it can be an option if safety is the first priority in your mind.
How much do generators cost?
The value of a generator can variety from hundreds to lots of dollars, with standby mills being the most high-priced of all. For a desk bound generator, you may anticipate to pay around $2,000 to your unit, and in all likelihood greater than $10,000.
For transportable turbines, you may pay anywhere from a few hundred dollars to heaps of greenbacks.
The best news is that they’re smooth to shop for — you can discover them at any domestic development save, consisting of domestic depot, Lowe’s, ace hardware and more.
The concept of a generator
There are many things to consider when buying a elverk. Below, we will talk about some important considerations that can help you make your decision.
Power is needed
One of the most important factors in choosing a generator is the amount of power you need. You can answer this question by considering what you will be using the generator for.
Portable generators produce less power and may be suitable for powering smaller items.
When you’re evaluating generator options, you need to think and calculate what equipment you think is essential to the continuity of services. A refrigerator needs about 600 watts, your sump pump (useful in flood zones) needs from 1,300 to 2,150 watts to start and about 800 to 1,000 watts to run.
For those in colder climates, a portable heater may need up to 1,500 watts. Appliances small ones like our cell phones only need 10 watts to charge, so it’s negligible compared to the larger devices you’ll have to evaluate and measure which one is right for your needs.
Common use
It’s now not just about how a good deal strength you need your generator to supply, however also what you will be the use of it for. Deciding on a generator to strength your private home in an outage may be very one of a kind from deciding on one to take on a tenting journey.
As we said, standby mills are completely established in your private home and provide backup electricity all through blackouts.
Fuel source
There are generally three different ways you can fire up your generator. The options available to you depend on the type of generator you choose and the specific model. First, gasoline is the most commonly used fuel for portable generators. Propane can be used to fuel both generators and portable generators.
Budget
The generator you choose will ultimately depend on your budget. Remember that stationary generators are expensive, while portable generators are generally more affordable.