The Condition of Urinary Incontinence
Numerous women are susceptible to urinary incontinence, especially after delivery or in old age. Several forms of incontinence exist, including:
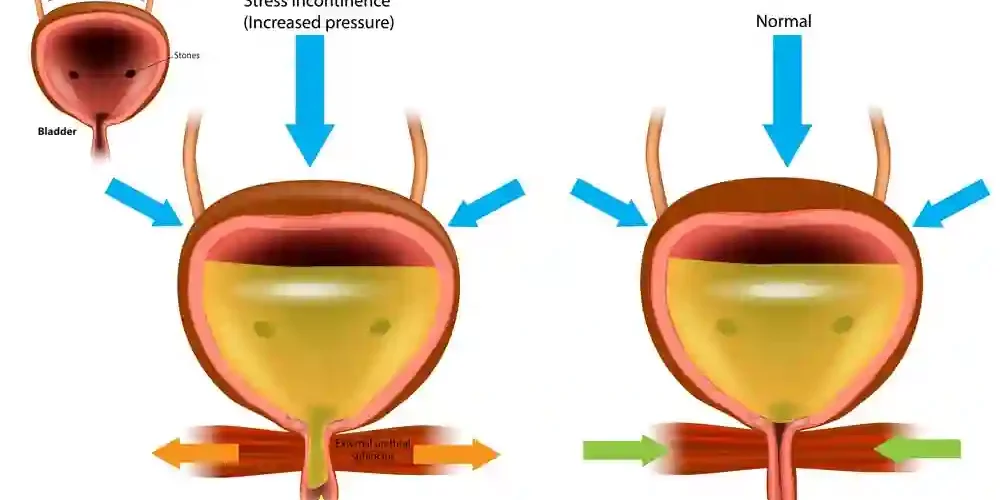
- Stress incontinence occurs when pee escapes due to physical movement or exertion, such as coughing, laughing, or sneezing.
- Urge incontinence is characterized by a sudden, urgent urge to urinate that is frequently uncontrollable. People with this form of incontinence typically require frequent urination.
- Mixed Incontinence – exhibiting both urge and stress incontinence
How do you treat urinary incontinence?
To alleviate symptoms, your doctor will initially recommend making adjustments to your lifestyle, such as losing weight and cutting back on alcohol and coffee. Pelvic floor exercises are also suggested to improve pelvic floor muscles, which frequently decrease after delivery or due to natural aging.
The use of incontinence items, such as pads, absorbent trousers, and hand-held urinals, is advantageous for many women. Occasionally, medication may be administered to alleviate symptoms.
If these techniques fail, you may be sent to bladder training, where a professional will instruct you on how to train yourself to hold your urine longer.
In certain instances, medicine or surgery may be the best alternative after all other methods have failed. Emsella Treatment Sheffield
Care for Urinary Incontinence
If alternative treatments for urinary incontinence symptoms have failed, you may be recommended for surgical intervention. There are a variety of minimally invasive surgical therapy techniques. These consist of:
- Mid-urethral tapes/slings constructed from synthetic material or the patient’s own tissue
- Injection of a bulking agent into the bladder’s neck
- Treatment of the bladder with Botox
- Colposuspension
When symptoms cannot be explained or are resistant to therapy, we may additionally explore the bladder using a modest surgical technique. This is known as a cystoscopy and includes using a tiny, thin camera to examine the bladder’s inside.
Stress and Incontinence Treatment Alternatives
Our team of physicians and women’s health physiotherapists will prescribe stress incontinence therapy depending on various health parameters, including age, condition, and the severity of urine symptoms.
Occasionally, a bladder operation may be required, although these operations are regularly performed with manageable side effects and often have a rapid recovery period with the proper aftercare. Below is additional information regarding incontinence remedies. Bristol Emsella
Mid-urethral Sling Operation
Stress incontinence is caused by physical exertion such as sneezing, lifting, or coughing. Midurethral tapes can be used to treat this condition.
This is a minimally invasive treatment in which tape is placed through a tiny incision in the vagina and threaded behind the urethra to prevent urine leakage. Typically, the surgery lasts between 15 and 30 minutes and is performed under general anesthesia.
Why would one opt for a Mid-urethral Sling procedure?
Current information indicates that tape methods have a high success rate (85-90%) and can continue for over 15 years. The National Institute for Clinical Excellence recommends this technique (NICE). It is regarded as one of the gold standard methods for the treatment of stress urine incontinence and has a lengthy history of evidence from the best quality scientific research demonstrating outstanding success rates and little hazards.
It is also a minimally invasive treatment requiring just minor incisions, resulting in minimum or no visible scars.
What dangers are associated with mid-urethral sling procedures?
All methods to restore continence can have an influence on the urine flow, although this is often imperceptible, and only 3 to 5 percent of women are unable to empty their bladder following the surgery. Depending on the etiology, the condition is reversible in nearly all of these instances.
After surgery to treat incontinence, a woman may feel the desire to urinate more frequently, although this feeling typically subsides over the post-operative recovery period. On rare occasions, a woman may need medication to quiet her bladder.
Although synthetic mid-urethral slings are suggested as a first-line treatment for stress incontinence, their usage has been halted in the United Kingdom. This indicates that we do not offer this service at this time.
Upon completion of a national evaluation, it is anticipated that we will be allowed to perform this operation, however until then, we continue to offer the procedure using a sling made from the patient’s own tissue, known as the Autologous Fascial Sling.
This needs a little bigger incision over the patient’s abdomen in order to manufacture a sling from the muscular sheath. It is introduced similarly to the mid-urethral tape.
Urethral Volumentensive Agents
What is the technique for Urethral Bulking Agents?
This method includes injecting a chemical into the urethral walls, near the neck of the bladder. The goal of the surgery is to enlarge the urethral walls so that the urethra can seal more firmly.
Women with stress incontinence or those who have trouble emptying their bladders are advised to undergo bulking operations. Additionally, it can be utilized in more difficult circumstances, such as in women who have undergone previous continence surgeries.
This is a brief operation performed under general anesthesia that involves neither incisions nor stitches. Typically, women may return home the same day.
However, it does not have the same success rate or long-lasting effects as mid-urethral tape or colposuspension, hence it is often considered a second-line therapy. Since bulking drugs wear off with time, multiple injections are frequently required.
What hazards are associated with Urethral Bulking Agents procedures?
Possible dangers include:
- Urinary burning or bruising, which often subsides quickly following therapy.
- Difficulty with bladder voiding
- Urethra Ache
- Urinary tract disease
Colposuspension Operations
What is the technique for Colposuspension?
Colposuspension is an antiquated treatment for urinary incontinence. It has a high rate of success and is performed by creating an incision in the abdomen, raising the vagina, which in turn elevates the neck of the bladder, and then suturing the bladder in its new, elevated position.
This is a more intrusive operation requiring a 45-to-60 minute procedure and a 3-4 night hospital stay. This treatment is less prevalent in the current day due to longer healing times and scarring, similar to a scar from a cesarean section. Newer mid-urethral tape techniques, which have a shorter operating time, quick recovery, and low scarring, are currently the most preferred treatment choice.
However, if a prior continence procedure has failed, a subspecialist urogynecologist may consider colposuspension.
What hazards are associated with Colposuspension procedures?
Colposuspension carries the same dangers as mid-urethral tape, as well as extra concerns associated with it being a more invasive operation, such as inability to completely empty the bladder, recurrent UTIs, and painful sex.
Because the treatment is not performed through the vagina, there are no hazards connected with vaginal healing.
Visit our patient resources page for further information about incontinence procedures.
Stress-Incontinence Operation
Before proceeding with an incontinence operation, all of our patients are presented with information outlining the various alternatives, the evidence supporting their success, the risks and advantages of each treatment, so that they may make an educated decision.
Botox administered to the Bladder
When is Botox administered to the bladder?
If medicine has failed to regulate a “unstable” bladder, Botox therapy may be recommended. Botulinum toxin A (Botox) is injected into the sidewalls of the bladder during this surgery to treat urge incontinence or overactive bladder syndrome.
This is a brief process that does not require incisions or stitches. It includes injecting Botox into the bladder wall using a cystoscope camera. After passing urine, you may return home the same day.
Botox’s effects typically last between three and twelve months, and treatment can be repeated if it proves beneficial.
What concerns does Botox pose to the bladder?
Although the long-term consequences of this medication are mostly understood, the following hazards are known:
- Urinary tract disease
- Difficulties in bladder emptying
Why should you consult a Subspecialist Urogynecologist?
A qualified subspecialist urogynecologist is educated to address urinary issues in women with the utmost proficiency. They work at centers where patients with complex issues are referred from other units, such as women who have been previously operated on or treated unsuccessfully for urine incontinence or prolapse.
In addition, they treat women with many types of incontinence or with incontinence and other pelvic floor issues, such as prolapse of the vagina and uterus. Typically, subspecialists are involved in the teaching of surgeons and the development of novel methods. Therefore, you are receiving the best quality of care possible.